Home >> Slide >> Fiber-Lube Bushings >> CJ/FCJ Fiber-Lube
CJ/FCJ Fiber-Lube
Daemar’s CJ/FCJ Fiber-Lube composite bushings allow true self lubrication. Ideal for long-term highly loaded applications. Additional benefits include: low friction values and resistance to corrosion.
Product Description
The DMR Fiber Wound (CJ/FCJ) Series bearing are ideal for non-lubricated, high load applications in a variety of climates and operating environments, exhibit a high load capacity similar to bronze, powdered metal and steel, and provide longer wear and extended operating life without the cost associated with lubrication.
Fiber wound bearings are available with thick walls for drop in replacement of steel and bronze bearings. Fiber wound bearings won’t rust like metal components, so you can use them in environments where traditional metals corrode and fail. You will find DMR Fiber wound bearing material in heavy agricultural, automotive, construction, industrial, marine, railway, and material handling equipment.
FCJ bearings are the ideal choice for combination motion-oscillatory, linear, and /or rotary applications. Their ability to run successfully against mild steel shafting makes a cost competitive system. Their versatility makes them excellent general purpose self-lubricating bearings.
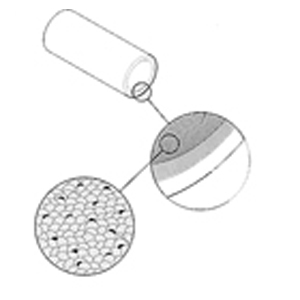
Product Design
The FL (CJ) bushings is a multilayered structure. The innermost layer consists of a synthetic fiber/PTFE layer. The second layer consists of epoxy coated high angle glass filaments. The outermost layer consists of epoxy coated low angle glass filaments.
The synthetic and PTFE fibers used in the liner have a long history of successful use as a bearing wear surface for rod end and aircraft spherical bearings. The high-load capacity and reliability of these bearings has made them the preferred design for many applications.
Fiberglass/epoxy filament wound bushings were originally developed for use as pressure vessels and rocket motor cases. Their light weight, high strength, and fatigue resistance make them ideal materials for structural applications, When used to make a bearing in this material allows the selection of fiber angles to provide optimum strength and rigidity. The resulting structure has a modulus of elasticity (13.79GPa) placing it in an intermediate area between rigid metals and soft plastic. It is rigid enough to support heavy loads, and at the same time compliant enough to tolerate moderate amounts of shaft misalignment without highly stressing the bearing corners.
The bearing wall acts like a spring and the thicker the wall section of the bearing the greater the deflection for a given load. This allows thick wall bearings to tolerate greater shaft misalignment.
The wear surface will support the shaft primarily as a function of the load rather than the shaft clearance. As load is applied, the wear surface will conform to the shaft assuring a large contact area. In contrast, the contact area of metal bearings decreases sharply as shaft clearances increase, and increase only slightly with load.
Typical Applications
FL-CJ
Backhoes
Front end Loaders
Marine davits/sheaves
Valve stem bushings
Hitches
Hydraulic cylinder pivots
Graders
Mining Equipment
Vending machines
FL-FCJ
Material handling equipment
Packaging machinery
Farm implements
Spreaders
Marine pivots
Robotics
Business machines
Linear bearings
Amusement park rides
Typical Specifications
Recommended Operating Limits and Engineering Information
CJ Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Pressure (P) | Static – psi 60,000 MPa 414 Dynamic – psi 30,000 Mpa 207 |
| Maximum Velocity (V) (no load) | ft/min – 150 m/sec – .76 |
| Lubrication | No |
| Temperature (Typical Range) |
-320/+300°F -195/+149°C |
| Shaft Hardness (Minimum, Rockwell Scale) |
Rc 50 |
| Shaft Finish (Recommended Ra, Microinches) |
8-16 |
| Shaft Material | Steel |
| Coefficient of Friction (Static/Dynamic Range) |
.02-.25 |
| Water Absorption (ASTM D570) |
<.5% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent |
| Linear of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (ASTM D696) 78°F to 300°F 26°C to 149°C |
in/in/°F 7×10-6 cm/cm/°C 13×10-6 |
FCJ Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Pressure (P) | Static – psi 20,000 MPa 138 Dynamic – psi 20,000 Mpa 140 |
| Maximum Velocity (V) (no load) | ft/min – 500 m/sec – 2.54 |
| Lubrication | No |
| Temperature (Typical Range) |
-320/+300°F -195/+149°C |
| Shaft Hardness (Minimum, Rockwell Scale) |
Rb 25 |
| Shaft Finish (Recommended Ra, Microinches) |
8-16 |
| Shaft Material | Steel |
| Coefficient of Friction (Static/Dynamic Range) |
.01-.20 |
| Water Absorption (ASTM D570) |
<.5% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent |
| Linear of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (ASTM D696) 78°F to 300°F 26°C to 149°C |
in/in/°F 7×10-6 cm/cm/°C 13×10-6 |








